North Korean hackers stole $2.2 billion in crypto this year


crypto thefts surged to $2.2 billion in 2024, representing a 21% rise compared to the previous year.
According to a Dec. 19 report by Chainalysis, this increase is closely tied to a growing wave of hacking activity, particularly by North Korean-linked cybercriminal groups.
Escalation in hacking activity
The crypto sector experienced 303 hacking incidents in 2024, up from 282 in 2023. These attacks resulted in significant losses, with the bulk of stolen funds — $1.58 billion — taken between January and July. This period accounted for 72% of the total amount stolen in 2024, reflecting an 84% surge compared to the same timeframe in 2023.
Unlike in prior years, centralized exchanges bore the brunt of these attacks, overtaking DeFi platforms as the primary target. Notable incidents included a $305 million breach of DMM Bitcoin in May and a $235 million hack of WazirX in July.
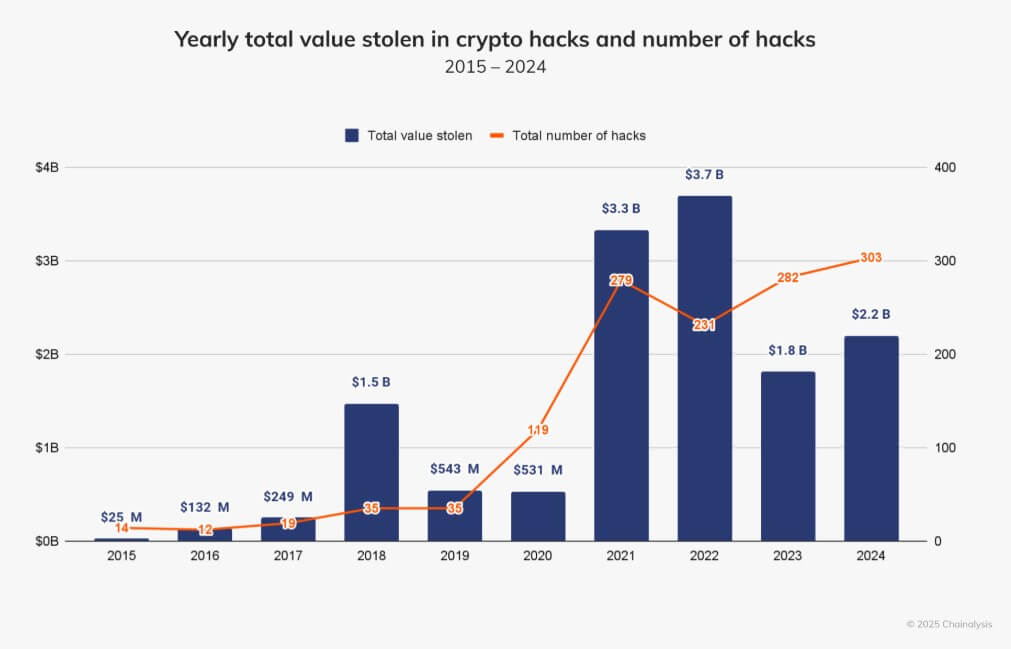
Chainalysis identified private key compromises as a major vulnerability, with these exploits contributing to nearly 44% of all stolen funds in 2024. Meanwhile, hackers often funnel these stolen assets through decentralized exchanges, mixing services, and blockchain bridges to obscure their activities and hinder tracking efforts.
North Korea leads crypto heists
North Korean hackers reached new heights in 2024, stealing $1.34 billion across 47 attacks.
These operations accounted for 61% of total funds stolen in the year and marked a staggering 103% increase from the $660 million attributed to North Korea in 2023. The data also revealed a faster pace of attacks, particularly those involving more significant sums exceeding $50 million.
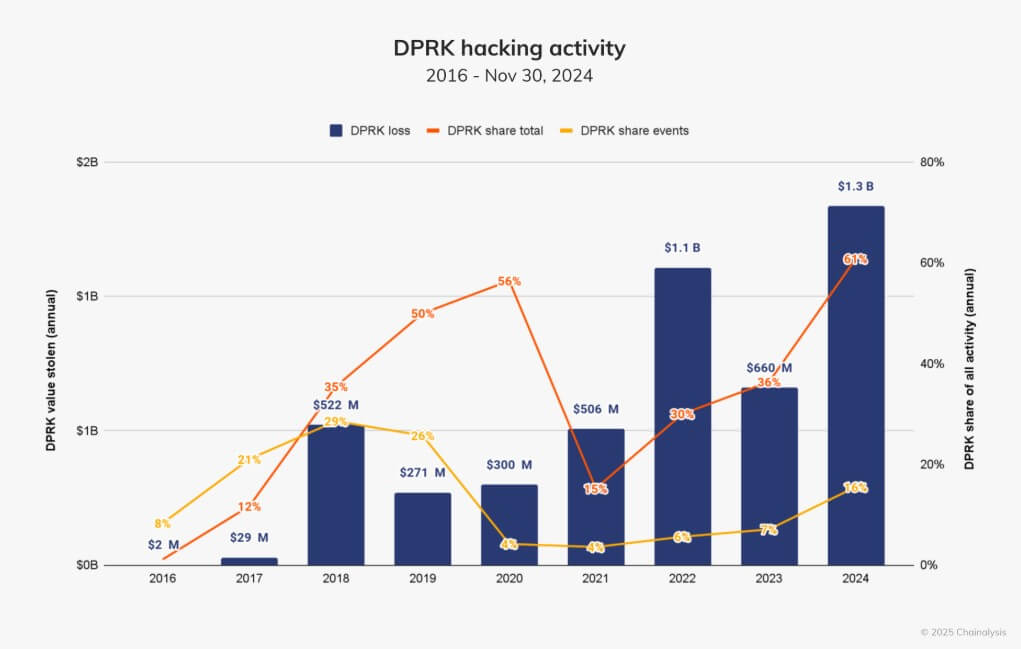

However, geopolitical developments might have influenced these activities.
Following a summit in late June between Russian President Vladimir Putin and North Korean leader Kim Jong Un, the value stolen by North Korean hackers declined noticeably. The average daily amount dropped by nearly 54% after July 1.
Meanwhile, non-North Korean thefts saw a slight increase after this period, suggesting a potential shift in focus for the DPRK, possibly tied to its growing military and technological collaboration with Russia.
Mentioned in this article


